Women’s Health
Gynecology
- Annual examination and Pap smear
- Colposcopy for abnormal pap smear results
- Contraception (including birth control pills, Intra Uterine Devices (IUD) and more)
- Treatment of pelvic pain, and irregular menstrual cycles
- STD screening
- O-shot (PRP and/or Exosomes procedure) for vaginal rejuvenation, vaginal dryness, sexual arousal, urinary incontinence


Breastfeeding
Breastfeeding consultations are a valuable resource for new parents. Dr. Anna Shlugman is a Certified Lactation Consultant with more than 15 years of experience in lactation and breastfeeding assistance. She helps with breastfeeding challenges and provides support and education on best practices.
Here are some key areas a breastfeeding consultation might cover:
- Latch and Positioning: Ensuring that the baby is latched on properly and positioned comfortably can prevent pain and promote effective breastfeeding.
- Feeding Techniques: Guidance on how to breastfeed efficiently, including how often and how long to feed.
- Milk Supply: Addressing concerns about milk production, including tips for increasing supply if needed.
- Pain Management: Offering solutions for common issues like sore nipples or engorgement.
- Feeding Plans: Developing a feeding plan that fits with the family’s lifestyle and needs.
- Troubleshooting: Identifying and resolving any problems that might arise, such as difficulties with baby’s weight gain or issues related to the mother’s health.
- Emotional Support: Providing encouragement and reassurance, as breastfeeding can sometimes be challenging both physically and emotionally.
- Weaning Advice: Guidance on transitioning from breastfeeding to other feeding methods when the time comes.
Consultations can be in-person, over the phone, or through video calls, depending on what works best for the family.
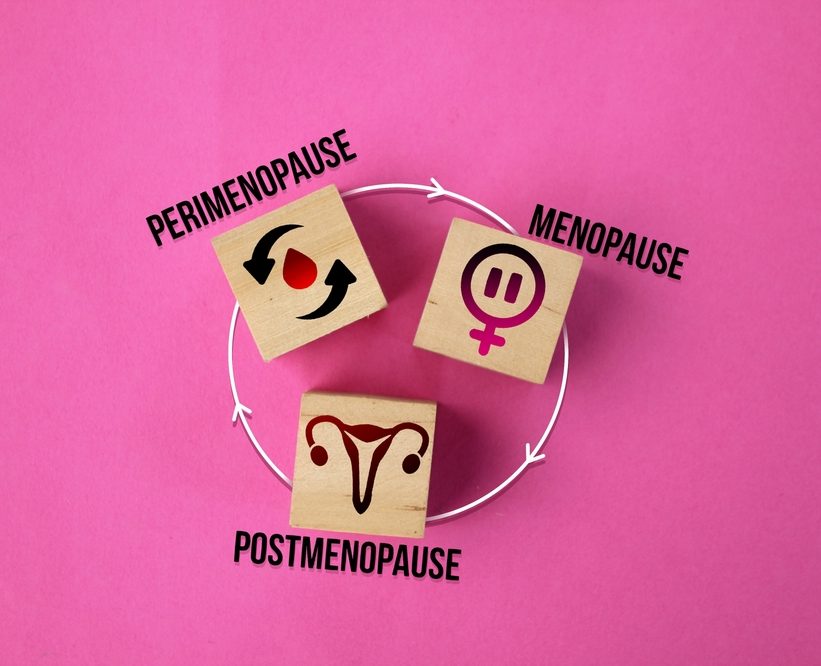
Menopause & perimenopause management
Managing menopause and perimenopause involves addressing a range of physical and emotional changes that occur as a person transitions from their reproductive years to menopause. Here are some strategies and approaches for managing these stages
- Perimenopause: The transition period leading up to menopause, often beginning in a person’s 40s but can start earlier. It lasts until menopause is confirmed, characterized by irregular periods and fluctuating hormone levels.
- Menopause: Defined as having gone 12 consecutive months without a menstrual period. The average age for menopause is around 51, but it can vary.
- Diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D can help with bone health. Foods rich in phytoestrogens (like soy) may help balance hormones.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity helps with mood regulation, weight management, and bone density. Aim for a mix of cardiovascular, strength, and flexibility exercises.
- Stress Management: Practices like yoga, meditation, and deep breathing can help manage stress and improve emotional well-being.
- Hot Flashes: Can be managed with lifestyle changes (e.g., dressing in layers, avoiding triggers like hot drinks and spicy foods) and sometimes medication. Some people find relief from herbal supplements, though it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider before starting any new treatment.
- Sleep Disturbances: Establishing a consistent sleep routine, creating a comfortable sleep environment, and avoiding caffeine or heavy meals before bed can help improve sleep quality.
- Mood Changes: Counseling, therapy, and support groups can provide emotional support. Sometimes, medication may be considered if mood changes are severe.
- Antidepressants: Certain SSRIs or SNRIs can help with mood swings and hot flashes.
- Gabapentin: Sometimes used to manage hot flashes, particularly in those who cannot use hormone therapy.
- Vaginal Moisturizers and Lubricants: Can help alleviate dryness and discomfort during intercourse.
- Local Estrogen Therapy: Applied directly to the vaginal area to relieve dryness and atrophy.
- Calcium and Vitamin D Supplements: Can help maintain bone density. Weight-bearing exercises are also beneficial.
- Bone Density Testing: Regular screenings may be recommended to monitor bone health.
- Screenings: Regular mammograms, pelvic exams, and other screenings as recommended by your healthcare provider.
- Health Monitoring: Keeping track of any new symptoms and discussing them with your healthcare provider to adjust management strategies as needed.
- Educational Resources: Books, online resources, and workshops can help you stay informed about menopause and perimenopause.
Bio-identical Hormone Replacement Therapy (BHRT) is a treatment approach that uses hormones chemically identical to those naturally produced by the body. BHRT is often used to address symptoms associated with menopause, perimenopause, and hormonal imbalances. Here’s a closer look at what BHRT involves
What is BHRT?
- Bio-identical Hormones: These are hormones that have the same chemical structure as those the body produces naturally. Common bio-identical hormones include estradiol, estrone, progesterone, and testosterone.
- Forms of BHRT: Hormones can be administered in various forms, such as pills, patches, gels, creams, injections, or pellets.
Benefits of BHRT
- Symptom Relief: BHRT is used to alleviate symptoms of menopause, such as hot flashes, night sweats, vaginal dryness, and mood swings.
- Customizable: The therapy can be tailored to individual needs based on hormone levels and symptoms.
- Fewer Side Effects: Some proponents believe bio-identical hormones may have fewer side effects compared to synthetic hormones because they are identical to natural hormones.
Types of BHRT
Estrogen Therapy
Estradiol
A primary form of estrogen used to treat menopausal symptoms.
Estrone and Estriol
Other forms of estrogen that may be used, often in combination
Progesterone Therapy
Micronized Progesterone
A bio-identical form of progesterone that may be used to balance estrogen levels and protect the uterine lining.
Testosterone Therapy
Used in some cases to address low libido and energy levels, although it is less commonly prescribed for women compared to estrogen and progesterone.
Combination Therapies
Sometimes, a combination of estrogen, progesterone, and/or testosterone is used to address various symptoms and hormonal imbalances
Administration Methods
- Pills: Oral bio-identical hormones.
- Patches: Adhesive patches that release hormones through the skin.
- Gels and Creams: Applied topically to the skin.
- Injections: Hormones administered via injection.
- Pellets: Small pellets inserted under the skin that release hormones over time.
Considerations and Risks
Individual Variability
Response to BHRT can vary widely among individuals. Regular monitoring and adjustments may be necessary.
Safety and Efficacy
While bio-identical hormones are often marketed as being safer than synthetic hormones, scientific evidence supporting their superiority is limited. BHRT should be prescribed and monitored by a healthcare provider.
Potential Risks
Like all hormone therapies, BHRT carries risks, including increased risk of blood clots, stroke, and certain cancers. The risks may depend on individual health factors and the specific hormones used.
Customized Approach
Blood/Saliva/Urine tests are done to measure hormone levels and tailor the therapy to meet individual needs.
Monitoring and Follow-Up
- Regular Check-Ups: Ongoing monitoring of hormone levels and overall health is important to ensure the therapy is effective and to manage any potential side effects.
- Adjustments: Dosages and forms of hormones may need adjustment based on symptoms and lab results.
